
Electronic Mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices.

Electronic Mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices.
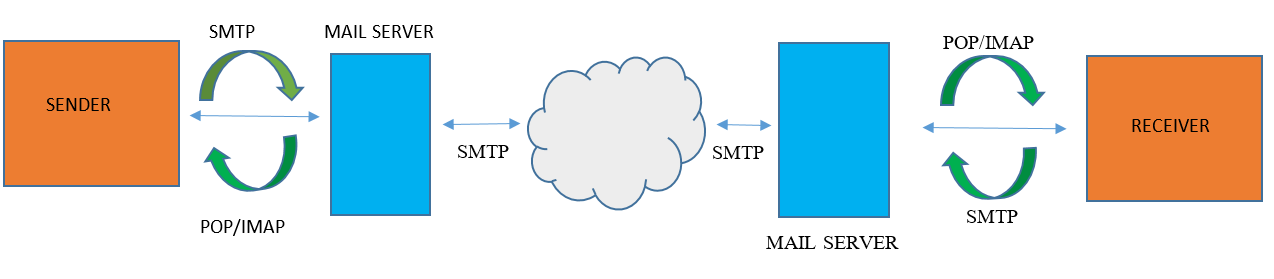
An MUA or Mail User Agent is the program that an end user uses to read and process mail. Typical examples include Mozilla Thunderbird, Microsoft Outlook, Eudora Mail, Incredimail or Lotus Notes. Sometimes it is called an email client.
An MTA, or Message Transfer Agent is the software and other systems that are responsible for sending and receiving mail between systems such as sendmail, postfix, qmail. That is the only thing MTAs do they send and receive messages between systems. MTAs use the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) to send and receive messages.
SMTP is part of the application layer of the TCP/IP protocol. SMTP is a standard communication protocol for sending email messages on business networks and the Internet. SMTP was originally developed in the early 1980s and remains one of the most popular protocols in use worldwide.MUAs and MTAs use this protocol for sending emails.
An MDA is a Mail Delivery Agent. MDAs are the software responsible for receiving a message from an MTA and arranging for it to be received by the local system (e.g. delivered to a mailbox). Any program that actually handles a message for delivery to the point where it can be read by an email client application can be considered an MDA. There are two main protocols used for retrieving email on an MDA:
MUAs use this protocol for receiving their emails from the final server. The Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) is a mail access protocol used by a client application to read messages from the mail server. Received messages are often deleted from the server. POP supports simple download-and-delete requirements for access to remote mailboxes (termed mail drop in the POP RFC's).
MUAs can use this protocol to send and receive emails on the servers. The Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) provides features to manage a mailbox from multiple devices. Small portable devices like smartphones are increasingly used to check email while travelling, and to make brief replies, larger devices with better keyboard access being used to reply at greater length. IMAP shows the headers of messages, the sender and the subject and the device needs to request to download specific messages. Usually mail is left in folders in the mail server.
SMTPS (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Secure) is a method for securing SMTP with TLS (transport layer security). It provides authentication of the communication partners, as well as data integrity and confidentiality.
Because the SMTP standard sends email without using encryption or authentication, every message that has been sent is exposed to view. This can cause various email security threats such as:
Client-side solutions such as Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (S/MIME) or pretty good privacy (PGP) can solve this problem, but they require users’ involvement. A better place to focus security efforts is on securing SMTP. STARTTLS is the ESMTP keyword used to initiate a secure SMTP connection between two servers using the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) (also known as TLS).
It is an SMTP security extension. It enables SMTP Client and Server to negotiate use of Transport Layer Security (TLS). Once the connection has been successfully established all further communication between the two servers is encrypted. This means that the source and destination email address and the entire message contents are all encrypted during transfer.
SMTP MTA-STS (SMTP Mail Transfer Agent Strict Transport Security) is a proposed standard that makes it possible to send downgrade-resistant email over SMTP. In that sense, it is like an alternative to DANE. It does this by being carried by the browser Certificate Authority model. SMTP MTA-STS is a mechanism enabling mail service providers to declare their ability to receive Transport Layer Security (TLS) secure SMTP connections, and to specify whether sending SMTP servers should refuse to deliver to MX hosts that do not offer TLS with a trusted server certificate.
Email Safeness Scorer: A privacy preserving machine learning based Client-Side (Mozilla Thunderbird Pugin) to provide safeness score of an email for alerting the user about possible phishing, scam etc.
The email safeness scorer gives the safeness score of the emails based on its content, the low safeness score signifies the dubious, scam, phishing, malicious or spam emails, whereas the high score tells that the email is safe i.e. the email is free from malicious intentions. Nowadays, emails have become a common means of sharing information. Malicious users use this medium for sending unsolicited messages for either advertising their product and services or for enticing gullible users for sharing their important information. This kind of message is generally referred to as spams. Spams are undesired emails, which are unsolicited bulk messages sent through email for advertising, phishing or inflicting malware on the recipient system.